Just to recap, here is a list of tools that we have been using for network forensics:
ChaosreaderChaosreader can extract images from the network log files (though not all as we saw) and will print out a nice html report of all the flows.
Here is Chaosreader in action:
Full ScreenIt can provide a nice start for making sense of the log file and locating connections of interest. However it doesn't extract all files of interest.
EtherapeEtherape allows you to see the traffic as a graphical representation. You can have it listen on a live device, or you can feed it a network dump file. Here is a video of etherape:
Full Screenp0fp0f is a passive OS identification tool. It uses three tests:
1) SYN packet test, where it watches outgoing SYN packets
2) Using the -A switch enables the SYN+ACK test
3) Using the -R switch enables the RST+ACK test
You can have it run on an interface by using the -i switch and interface name, or against a dump file using the -s flag.
snortSnort is an intrusion detection system, but can also be used to read files. You have been supplied with alert files that were created by snort against the dump files given to you. When running snort you can use flags to make it read in a file. Here are the flags that were used to create the alert files:
# snort -c [config_file] -r [dump_file] -l [directory]
-c lets snort know which configuration to use
-r lets snort know which file to read
-l lets snort know where to write the log files
A brief snort video:
Full ScreentcpdumpTcpdump can be used to capture network traffic. When doing so, you let tcpdump know which device to use to read packets using the
-i switch. If you want to save the traffic, you can use the
-w switch. You can also specify the size of each packet saved by using the
-s switch. Here is an example usage:
# tcpdump -i eth0 -s 1515 -w file.lpc
Tcpdump can also be used to read traffic data from a network dump file by using the
-r switch followed by the name of the file you want to read. Here are some other switches you should use:
-n used to get only IP numbers
-nn don't translate IP and port numbers
-x used to get hex data of packets
-X used to get hex and ASCII data of packets
-c used to specify a number of packets
-e used to get link layer headers (MAC addresses)
One can also specify other items for tcpdump to look for in the traffic. Here is a TCP header:

With all TCP traffic there are flags that are associated with the conversation. Here are some flags of interest:
- SYN – Synchronize sequence numbers
- ACK – indicates an ACKnowledgment
- PSH – Push function
- RST – Reset the connection
- FIN - close connection
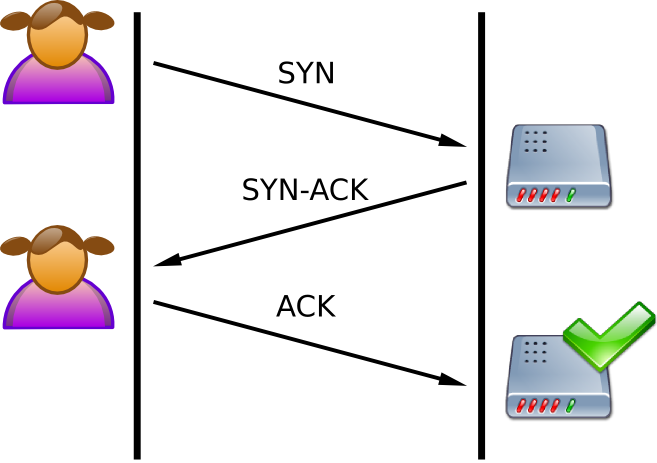
When a TCP connection is first made, there is a 3-way handshake that must occur before data can be sent. The handshake consists of:
1) A SYN packet sent to the server from the client
2) Response of SYN-ACK from the server
3) An ACK sent back to the server from the client
Seen below:
Therefore, one is often interested in SYN packets and can search for them using tcpdump. If you look at the TCP header you can see that the flags are located in the thirteenth byte. Therefore we can tell tcpdump to look in the thirteenth byte and give it the value. Since the SYN flag is the second one from the right, it has a value of 2 (think binary). So one usage is:
$ tcpdump -n -r [file.lpc] 'tcp[13]==2'
If you want to see packets with the SYN flag (and other flags) set you have to use bitwise AND:
$ tcpdump -n -r [file.lpc] 'tcp[13] & 2 == 2'
Likewise SYN+ACK has a value of 18, since the ACK flag is in location 4 (zero based) from the right which has a value of 16 and since SYN has a value of 2, we can change the total value to 18:
$ tcpdump -n -r [file.lpc] 'tcp[13]==18'
Or Hex:
$ tcpdump -n -r [file.lpc] 'tcp[13]==0x12'
You can also use the tcpflags option:
$ tcpdump -n -r [file.lpc] 'tcp[tcpflags]==2'
You can also indicate a particular host:
$ tcpdump -n -r [file.lpc] 'tcp[13]==2' and host [IP]
tcpxtractTcpxtract can be used to extract files from network dumps. We found that it crashed on some dumps with a segmentation fault however while we were doing our analysis.
tcpflowTcpflow is a really nice tool that can be used to rebuild conversations between two machines. Therefore we can use it to extract files. Here is a basic usage:
$ tcpflow -r [file.lpc] -c port [port number]
The
-r switch works as before to indicate which file to read. The
-c flag says put output to stdout. The
port option lets one indicate which port number to use to construct a stream.
Here is a video of tcpflow being used to extract a JPEG file after finding it with chaosreader:
Full ScreenTherefore, if you have a lot of ftp connections, you can extract all files from the streams by using
port 20 in the tcpflow command. Why port 20? Because an ftp connection uses two ports: 20 and 21. Port 21 is the control/command port (the connection all your typed commands go to) and port 20 is the data connection where the files get uploaded. You can use it on Venus, just issue the following commands:
$ wget
ftp://ftp.circlemud.org/pub/jelson/tcpflow/tcpflow-0.21.tar.gz
$ tar -xvzf tcpflow-0.21.tar.gz
$ cd tcpflow-0.21/
$ ./configure
$ make
The executable will be in the
tcpflow-0.21/src
folder:
 Wireshark et al.
Wireshark et al.You have been using wireshark for a while now. I will continue writing about it a bit later...
Full Screen


